R and S System Used in Which Isomerism
The symbol R comes from the Latin rectus for right and S from the Latin sinister for left. Regarding the S and R nomenclature nearly all amino acids in proteins are S at the alpha carbon.

Organic Chemistry Chirality R S Notational System Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
Oximes derived from ketones are ketoximes.
. A racemic mixture is named as RS. Pharmacological differences between R-- and S-ibuprofen Ibuprofen IBU is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug exhibiting optical isomerism. The R S system is an important nomenclature system for denoting enantiomers.
For example one of the optical isomers enantiomers of the amino acid alanine is known as alanine. Since most of the chiral stereogenic centers we shall encounter are. An achiralchiral high-performance liquid chromatographic system for the analysis of total warfarin together with the R- and S-enantiomers in clinical samples has been developed.
Major Role of CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 S Xue-Qing Li Lars Weidolf Roger Simonsson and. In in vitro studies it has been demonstrated that only the S-enantiomer inhibits the. The letter S comes from the Latin word Sinister.
The oximes exhibit geometrical isomerism due to the restricted rotation of the C N bond. Simple substances which show optical isomerism exist as two isomers known as enantiomers. RS System of Nomenclature Nomenclature of Absolute Configuration.
EnantiomerEnantiomer Interactions between the S- and R- Isomers of Omeprazole in Human Cytochrome P450 Enzymes. Are amino acids R or S. This system is based on certain rules called as sequence rules and also as CIP rules.
Rosanoff in 1906 is still used for naming amino acids and carbohydrates but it is not unequivocal in all cases and cannot easily be applied to all families of compounds. The stereocenters are labeled as R or S. The R S system is an important nomenclature system for denoting enantiomers.
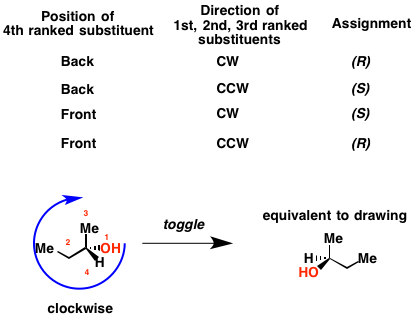
1 Using the R S system of nomenclaturedraw and name all of the isomers of hydrobenzoin 2Calculate the theoretical weight of sodium borohydride needed to. Consider the first picture. Number the four atoms or groups of atoms such that 1 has.
Note that the prefixes R and S refer to absolute rotation of plane-polarized light. When the center is oriented so that the lowest-priority substituent of the four is pointed away. The R and S designation indicates that the two are enantiomers.
This enantiomer is known as the form. The RS system is an important nomenclature system used to denote distinct enantiomers. It is called as R-S system as the prefixes R-and S-are used to designate the configuration at a particular chirality centre.
Only the racemate is in clinical use. Oximes derived from aldehydes are called aldoximes. The Sequence Rule and The Viewing Rule.
This approach labels each chiral center R or S according to a system by which its substituents are each assigned a priority according to the CahnIngoldPrelog priority rules CIP based on atomic number. Prefixes d- and l- are obsolete synonyms for - and -. Prioritize the four atoms or groups of atoms attached to the chiral center based on the atomic number of the atom that is bonded directly to the chiral center.
The sequence rule is the same as that used for assigning E-Z prefixes to double bond stereoisomers. Using the RS system of nomenclature draw and name all of the isomers of hydrobenzoin. A curved arrow is drawn from the highest priority 1 substituent to the lowest priority 4 substituent.
In aldoximes at least either R or R 1 is hydrogen. Another naming system uses the prefixes - and - to denote the enantiomers optical activity. R and S refer to the structural difference between stereoisomers.
Stereocenters are labeled R or S The right hand and left hand nomenclature is used to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. The letter R comes from the Latin word Rectus meaning Right-handed. What are R and S isomers.
In ketoximes both R or R 1 are alkyl or aryl groups only. S isomer has its relative direction of the priority order in an anticlockwise direction. This system is named as CIP Cahn Ingold Prelog system after their names.
The achiral analysis is achieved using a C8 column which is coupled to a chiral stationary phase alpha 1-acid glyco. RS System - Sequencing Rules The DL system proposed by M. A solution of one enantiomer rotates the plane of polarisation in a clockwise direction.
Metabolism S-warfarin is rapidly metabolized by oxidation to produce 6 hydroxy warfarin and subsequently reduced to warfarin alcohol R S a racemic mixture. Priority Rules for Naming Chiral Centers - The RS System 1. The higher the atomic number the higher the priority.
This approach labels each chiral center R or S according to a system by which its substituents are each assigned a priority according to the CahnIngoldPrelog priority rules CIP based on atomic number. The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog system is a set of rules that allows us to unambiguously define the stereochemical configuration of any stereocenter using the designations R from the Latin rectus meaning right-handed or S from the Latin sinister meaning left-handedThe rules for this system of stereochemical nomenclature are on the surface fairly simple. D and L d and l can only be measured by determining whether the substance rotates the polarization of polarized light clockwise or counterclockwise.
The assignment of these prefixes depends on the application of two rules. Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments 7th Edition Edit edition Solutions for Chapter 55 Problem 1Q.

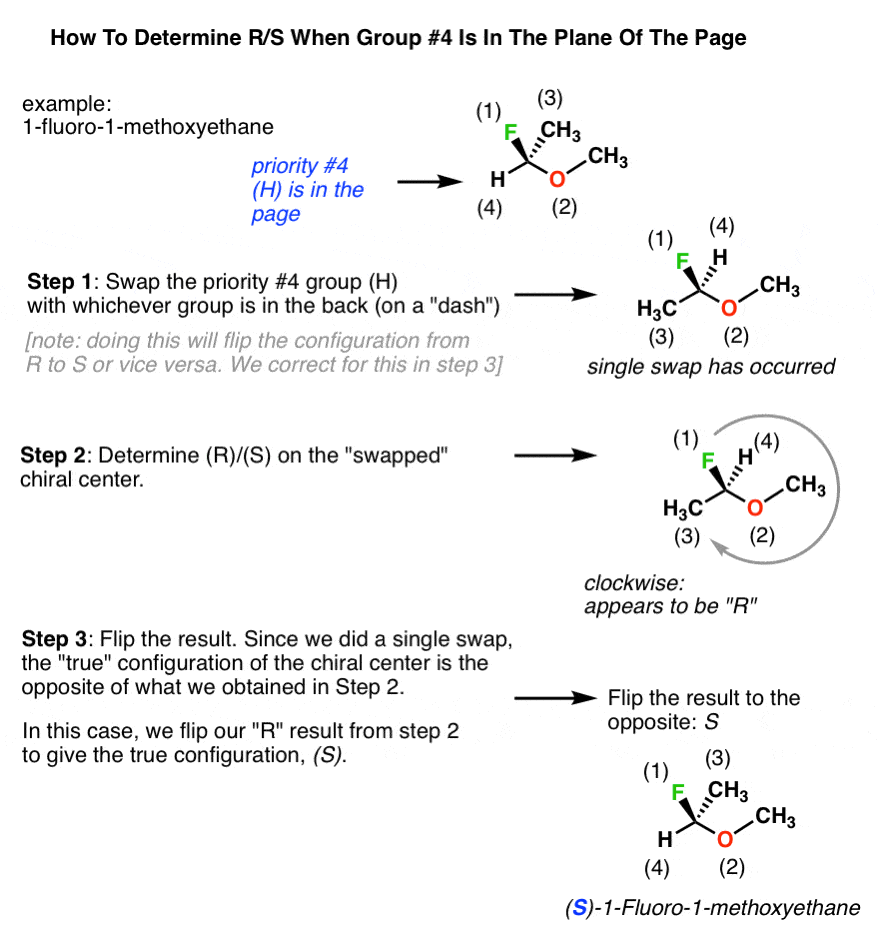
How To Determine The R And S Configuration Chemistry Steps

6 3 Absolute Configuration And The R And S System Chemistry Libretexts
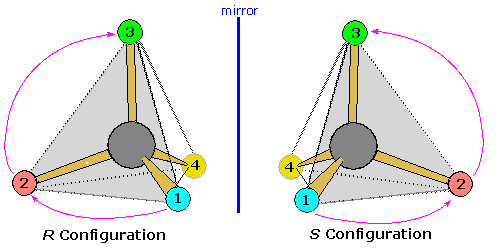
Introduction To Assigning R And S The Cahn Ingold Prelog Rules

How To Determine The R And S Configuration Chemistry Steps
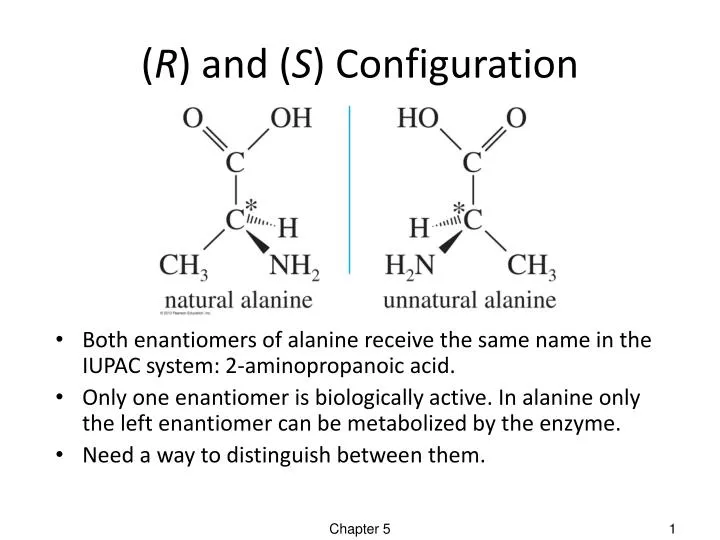
Ppt R And S Configuration Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2437795

Difference Between R And S Configuration Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
Rs System Of Nomenclature In Organic Chemistry
R S Nomenclature Organic Compounds Psiberg

Sequence Rules For R And S Nomenclature Youtube
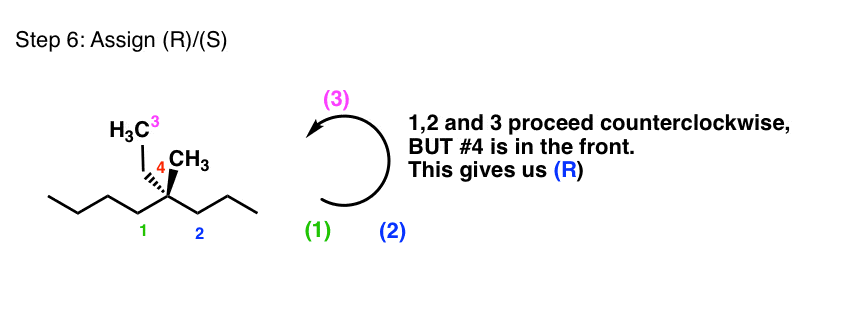
Introduction To Assigning R And S The Cahn Ingold Prelog Rules

Chapter 6 Chirality The Handedness Of Molecules Isomers

How To Determine The R And S Configuration Chemistry Steps
6 3 Absolute Configuration And The R And S System Chemistry Libretexts

R S System Clockwise Anticlock Wise Rectus Sinister

R S Optical Isomerism Explained Asymmetric Chiral Isomers Molecules Isomerism Mirror Image Forms Enantiomers Racemic Micture Racemisation Gce As A2 A Level Organic Chemistry Revision Notes
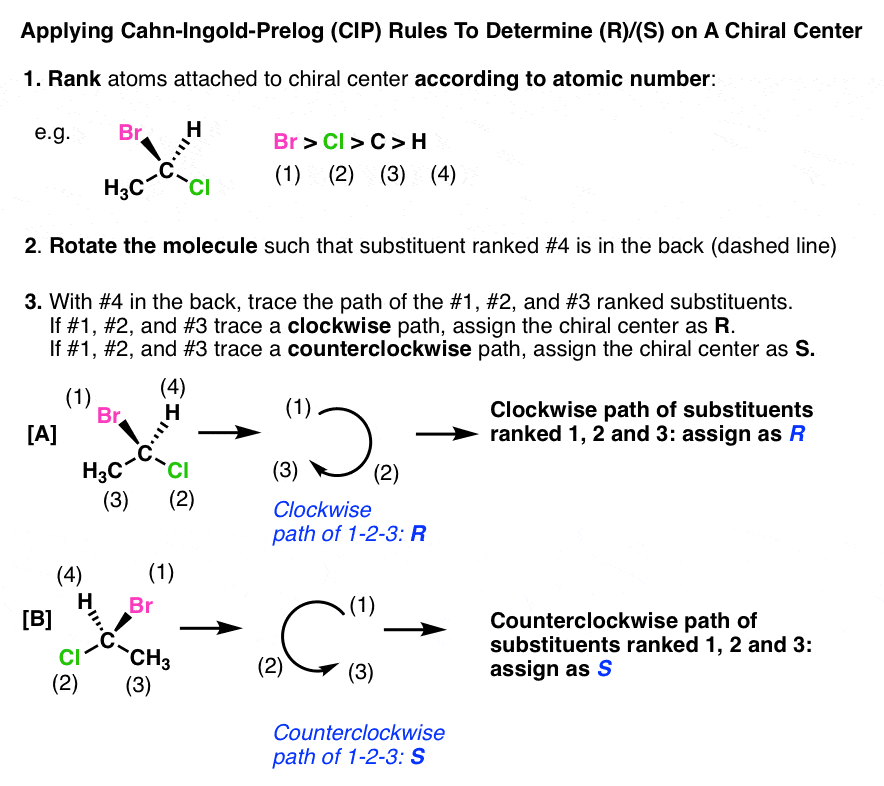
Introduction To Assigning R And S The Cahn Ingold Prelog Rules
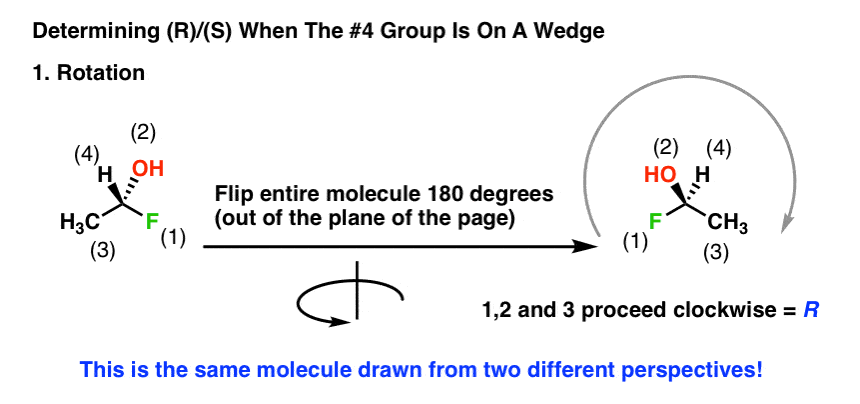
Introduction To Assigning R And S The Cahn Ingold Prelog Rules
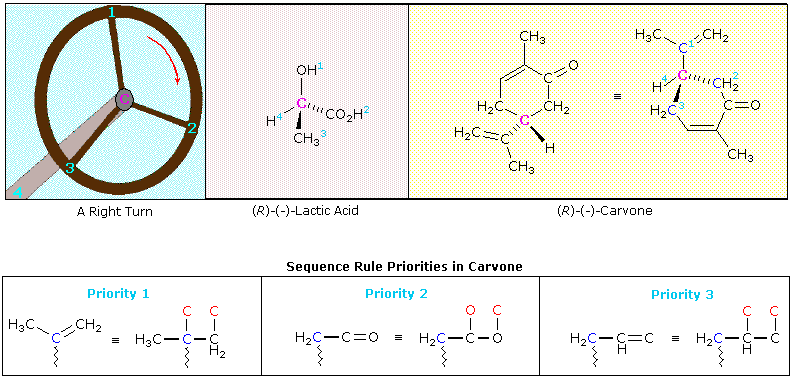
Comments
Post a Comment